A huge gamma-ray burst: Difference between revisions
imported>Hhudson (changed figures) |
imported>Hhudson No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|title = A huge gamma-ray burst | |title = A huge gamma-ray burst | ||
|number = 199 | |number = 199 | ||
|first_author = | |first_author = David Smith | ||
|second_author = | |second_author = Andre Csillaghy | ||
|publish_date = May | |publish_date = May 6, 2013 | ||
|next_nugget = | |next_nugget = [[Too few? Too many?]] | ||
|previous_nugget = [[Three-phase life leads to corpulent X-ray loops]] | |previous_nugget = [[Three-phase life leads to corpulent X-ray loops]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
shielding. | shielding. | ||
Accordingly a bright enough cosmic transient can readily be seen, and RHESSI has | |||
particularly good characteristics (high gamma-ray spectral resolution, | particularly good characteristics (high gamma-ray spectral resolution, | ||
high temporal resolution, and good livetime measurements). | high temporal resolution, and good livetime measurements). | ||
So it was not surprising | So it was not surprising that RHESSI has observations of the | ||
[http:// | [http://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/shocking-burst.html "shockingly bright"] | ||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma-ray_burst gamma-ray burst] that we | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma-ray_burst gamma-ray burst] that we | ||
report here. | report here (Ref. [1]). | ||
This particular burst appears to have originated from a supernova explosion | |||
at a [redshift] of about Z = 0.34, according to the many reports (69 at time of writing) from the | |||
many observatories that contribute to the | |||
[http://gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/gcn3_archive.html GCN archive]. | |||
These remarkable astronomical phenomena burst onto the scene secretly, detected originally | These remarkable astronomical phenomena burst onto the scene secretly, detected originally | ||
by the military [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vela_(satellite) Vela] satellites | by the military [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vela_(satellite) Vela] satellites | ||
| Line 40: | Line 44: | ||
[http://sprg.ssl.berkeley.edu/~tohban/wiki/index.php/RHESSI_Catches_Gamma-Ray_Bursts [3]]). | [http://sprg.ssl.berkeley.edu/~tohban/wiki/index.php/RHESSI_Catches_Gamma-Ray_Bursts [3]]). | ||
== | == GRB 130427A as seen by RHESSI == | ||
Figure 1 gives an overview of the time history of the burst on "long" time scales. | Figure 1 gives an overview of the time history of the burst on "long" time scales. | ||
| Line 46: | Line 50: | ||
RHESSI's limits, as imposed by photon arrival statistics. | RHESSI's limits, as imposed by photon arrival statistics. | ||
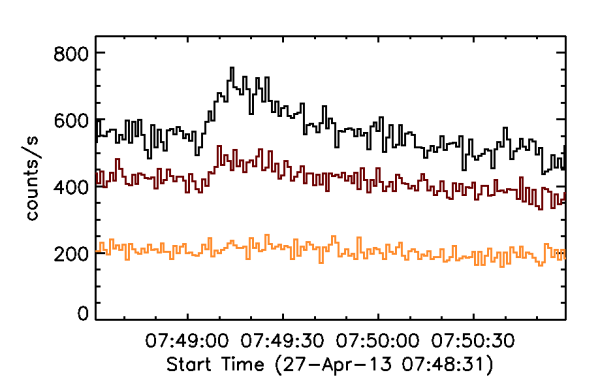
[[File: | [[File:199f2.gif|center|thumb|800px|Figure 1: | ||
Time series of RHESSI counts, in a preliminary view, for about 15 s during | Time series of RHESSI counts, in a preliminary view, for about 15 s during | ||
GRB 130427A. | GRB 130427A. | ||
Note the | The energy bands are 0.05-1, 1-5, and 5-15 MeV. | ||
The time resolution here is 25 ms, but higher resolution is available in the data | |||
because each photon's detection is time-tagged. | |||
Note the remarkably harder spectrum of the spikes of gamma radiation above | |||
5 MeV. | 5 MeV. | ||
]] | ]] | ||
| Line 55: | Line 62: | ||
With so much variability, with very large dynamic ranges in spectrum and | With so much variability, with very large dynamic ranges in spectrum and | ||
flux, it is hard to represent the data well. | flux, it is hard to represent the data well. | ||
The temporal binning in Figure 1 is 25 ms. | |||
The | |||
Figure 1 | |||
Note that RHESSI time-tags each photon's arrival time to about one μs and hence | Note that RHESSI time-tags each photon's arrival time to about one μs and hence | ||
is very flexible as regards binning. | is very flexible as regards binning. | ||
Note the hard spikes of gamma-ray emission above 5 MeV. | |||
Other reports on this event note that | |||
[http://fermi.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Fermi] could detect gamma-rays in its LAT detector, | |||
which set a new record on GRB photon energy of | |||
of | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fermi_Gamma-ray_Space_Telescope#GRB_130427A 94 GeV]. | ||
[[File:130427a_lateplot.png|center|thumbnail| | [[File:130427a_lateplot.png|center|thumbnail|600px|Figure 2: | ||
A later, slower burst, observed only at lower energies, about two minutes after the initial observation. | A later, slower burst, observed only at lower energies, about two minutes after the initial observation. | ||
]] | ]] | ||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
Solar X-ray and gamma-ray bursts can be bright, but the Sun is "very" close by | Solar X-ray and gamma-ray bursts can be bright, but the Sun is "very" close by | ||
astronomical standards. | astronomical standards. | ||
Other GRBs at truly cosmological distances have been detected; an indication of their | |||
huge gamma-ray luminosities. | |||
Th GRB fluxes may exhibit strikingly fast time variations (as in this case), and an | |||
amazing variety of time profiles. | |||
Nevertheless theorists often, in desperation perhaps when confronted by these | Nevertheless theorists often, in desperation perhaps when confronted by these | ||
amazing phenomena, may turn to solar paradigms for some of the explanations. | amazing phenomena, may turn to solar paradigms for some of the explanations. | ||
Or, at least the use of the word "flare"! | Or, at least for the use of the word "flare"! | ||
See Reference [ | It is very unlikely that a supernova explosion matches any solar paradigm very | ||
well, or at least we can hope that this doesn't turn out to be the case. | |||
See Reference [2] for a full account. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
[1] [http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2009ARA%26A..47..567G "Gamma-Ray Bursts in the Swift Era"] | [1] [http://gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/gcn3/14448.gcn3 GRB 130427A: Swift detection of a very bright burst with a likely bright optical counterpart] | ||
[2] [http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2009ARA%26A..47..567G "Gamma-Ray Bursts in the Swift Era"] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:53, 18 May 2013
| Nugget | |
|---|---|
| Number: | 199 |
| 1st Author: | David Smith |
| 2nd Author: | Andre Csillaghy |
| Published: | May 6, 2013 |
| Next Nugget: | Too few? Too many? |
| Previous Nugget: | Three-phase life leads to corpulent X-ray loops |
Introduction
RHESSI's lack of background-reducing collimation means that its Ge detectors can see most the entire gamma-ray sky, noting that the Earth looms large from low Earth orbit, blocking off a major fraction at any given time. Mostly the gamma-ray sky, though bright in absolute terms, is not detectable by RHESSI because of its lack of heavy anticoincidence shielding.
Accordingly a bright enough cosmic transient can readily be seen, and RHESSI has particularly good characteristics (high gamma-ray spectral resolution, high temporal resolution, and good livetime measurements). So it was not surprising that RHESSI has observations of the "shockingly bright" gamma-ray burst that we report here (Ref. [1]). This particular burst appears to have originated from a supernova explosion at a [redshift] of about Z = 0.34, according to the many reports (69 at time of writing) from the many observatories that contribute to the GCN archive.
These remarkable astronomical phenomena burst onto the scene secretly, detected originally by the military Vela satellites designed to record terrestrial tests of nuclear weapons. Note that we have already described RHESSI's observations of magnetars and GRBs in earlier Nuggets: ([1,] [2], [3]).
GRB 130427A as seen by RHESSI
Figure 1 gives an overview of the time history of the burst on "long" time scales. As will be seen in later figures, the time scales of variability range down to RHESSI's limits, as imposed by photon arrival statistics.
With so much variability, with very large dynamic ranges in spectrum and flux, it is hard to represent the data well. The temporal binning in Figure 1 is 25 ms. Note that RHESSI time-tags each photon's arrival time to about one μs and hence is very flexible as regards binning. Note the hard spikes of gamma-ray emission above 5 MeV. Other reports on this event note that Fermi could detect gamma-rays in its LAT detector, which set a new record on GRB photon energy of 94 GeV.
This event was caught by many observatories around the world, including the some of those in space. The RHESSI Browser shows the RHESSI time series in an overview, along with the striking detection by the Fermi GBM instrument. From this one can see that Fermi was in Earth's shadow at the time, while RHESSI was not - hence, the RHESSI data include many solar features.
Conclusions
RHESSI sees extreme events from all over the Universe, and there are some (perhaps coincidental) points of similarity. Solar X-ray and gamma-ray bursts can be bright, but the Sun is "very" close by astronomical standards. Other GRBs at truly cosmological distances have been detected; an indication of their huge gamma-ray luminosities. Th GRB fluxes may exhibit strikingly fast time variations (as in this case), and an amazing variety of time profiles. Nevertheless theorists often, in desperation perhaps when confronted by these amazing phenomena, may turn to solar paradigms for some of the explanations. Or, at least for the use of the word "flare"! It is very unlikely that a supernova explosion matches any solar paradigm very well, or at least we can hope that this doesn't turn out to be the case. See Reference [2] for a full account.
References
[1] GRB 130427A: Swift detection of a very bright burst with a likely bright optical counterpart