The Slowest Flare: Difference between revisions
imported>Hhudson No edit summary |
imported>Schriste No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|second_author = Hugh Hudson | |second_author = Hugh Hudson | ||
|publish_date = 23 July 2012 | |publish_date = 23 July 2012 | ||
|next_nugget = | |next_nugget={{#ask: [[Category:Nugget]] [[RHESSI Nugget Index::181]]}} | ||
|previous_nugget = | |previous_nugget={{#ask: [[Category:Nugget]] [[RHESSI Nugget Index::179]]}} | ||
[ | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 14: | Line 13: | ||
A remarkable flare, distinguishable by its very slow rise phase, has just | A remarkable flare, distinguishable by its very slow rise phase, has just | ||
occurred (SOL2012-07-17T17:15, M1.7) near the | occurred (SOL2012-07-17T17:15, M1.7) near the west limb of the Sun. | ||
According to the NOAA database | According to the [http://www.swpc.noaa.gov/ NOAA] database for the | ||
standard definitions of start and peak time, it took this flare 5.2 hours to | [http://www.swpc.noaa.gov/today.html GOES] X-ray photometers, using the | ||
develop. | standard definitions of start and peak time, it took this flare 5.2 hours to develop fully in the 1-8 Å soft X-ray band. | ||
We show an overview from SDO/AIA and RHESSI in Figure 1. | We show an overview from [http://aia.lmsal.com/SDO/ AIA] and RHESSI in Figure 1. | ||
Please refer to the extensive | Please refer to the extensive | ||
[http://sdowww.lmsal.com/sdomedia/ssw/media/ssw/ssw_client/data/ssw_service_120717_073119_84874/www/ movies] | [http://sdowww.lmsal.com/sdomedia/ssw/media/ssw/ssw_client/data/ssw_service_120717_073119_84874/www/ movies] | ||
| Line 27: | Line 26: | ||
by RHESSI at two different times during the long rise phase, separated by two hours. | by RHESSI at two different times during the long rise phase, separated by two hours. | ||
These images are not registered well, but by using the limb as a guide one can see that the initial | These images are not registered well, but by using the limb as a guide one can see that the initial | ||
RHESSI 12-25 keV brightenings were in the ribbon region to the lower left, and that later on the | RHESSI 12-25 keV (nonthermal or high-temperature) brightenings were in the ribbon region to the lower left, | ||
coronal sources dominated. | and that later on the coronal sources dominated the images. | ||
]] | ]] | ||
A skeptic might want to describe this as a coincidental | A skeptic might want to describe this very long-rise GOES event as a coincidental | ||
superposition of | superposition of weaker events, perhaps on different parts of the Sun, | ||
perhaps on different parts of the Sun, | but in fact the AIA movies linked above, and the RHESSI imaging, show that the entire flare | ||
but in fact the movies linked above show that the entire flare | |||
evolution consisted of a single organic process. | evolution consisted of a single organic process. | ||
A search of the GOES database reveals that in fact this event had the | A search of the GOES database reveals that in fact this event had the | ||
longest start-to-peak time interval of any M or X-class flare in | longest start-to-peak time interval of any M or X-class flare in | ||
the present [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_cycle Hale cycle], in fact | the present [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_cycle Hale cycle], in fact since 1995 (FIgure 2). | ||
[[File:180f2.png|thumb|left|300px|Figure 2: | [[File:180f2.png|thumb|left|300px|Figure 2: | ||
Histogram of the rise times (start to peak) of all of the tabulated GOES M-class and X-class flares | Histogram of the rise times (start to peak) of all of the tabulated GOES M-class and X-class flares | ||
since 1995. | since 1995. | ||
The red asterisk shows the location of our flare, | The red asterisk shows the location of our flare, definitely above the general trend of the histogram. | ||
]] | ]] | ||
| Line 55: | Line 53: | ||
pages). | pages). | ||
Furthermore, since this flare occurred near the west limb, an associated | Furthermore, since this flare occurred near the west limb, an associated | ||
CME almost always means an SEP - a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | CME almost always means an SEP - a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_energetic_particles solar energetic particle] event. | ||
This too was observed. | This too was observed. | ||
Finally, even better, another (more powerful and more impulsive) flare | Finally, even better, another (more powerful and more impulsive) flare | ||
| Line 64: | Line 62: | ||
an earlier slow ejection out in the [http://helios.gsfc.nasa.gov/heliosph.html heliosphere], in this case | an earlier slow ejection out in the [http://helios.gsfc.nasa.gov/heliosph.html heliosphere], in this case | ||
about halfway between the Sun and the orbit of Earth. | about halfway between the Sun and the orbit of Earth. | ||
That prediction, if fulfilled (or not), could lead to a future Nugget! | |||
== Energetics == | == Energetics == | ||
Such an event | Such an event may appear to have no [http://hesperia.gsfc.nasa.gov/hessi/flares.htm impulsive phase]; | ||
that is, no hard X-ray and microwave signatures of powerful energy release into non-thermal particle acceleration. | |||
The non-impulsive behavior here may or may not reflect the presence of non-thermal particles, | The non-impulsive behavior here may or may not reflect the presence of non-thermal particles, though, | ||
simply because the longer time scale of the event may make them | simply because the longer time scale of the event may make them less detectable | ||
less detectable | |||
This event, well-observed by both RHESSI and [http://fermi.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Fermi] in hard | This event, well-observed by both RHESSI and [http://fermi.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Fermi] in hard | ||
X-rays, provides an excellent test case for this question: can | X-rays, provides an excellent test case for this question: can | ||
slow CMEs also be associated with non-thermal energy release? | slow CMEs also be associated with non-thermal energy release? | ||
A detailed study of these data | A detailed study of these comprehensive data would be rewarding. | ||
In a sense the answer is obvious, because we can see the SEPs. | In a sense the answer is obvious, because we can see the SEPs. | ||
But do we see hard X-rays and/or microwaves as well? | But do we see hard X-rays and/or microwaves from the flare itself, as well? | ||
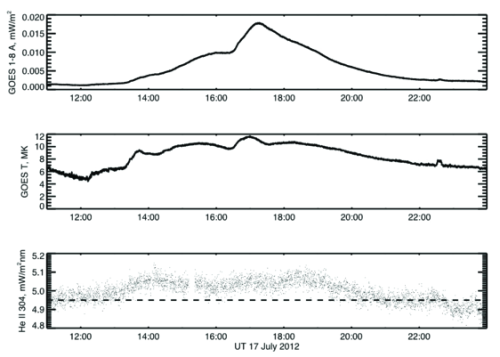
Figure 3 shows time series of GOES, the GOES temperature, and the | Figure 3 shows time series of GOES, the GOES temperature, and the | ||
[http://lasp.colorado.edu/home/about/quick-facts-sdo-eve/ EVE] observation of the | [http://lasp.colorado.edu/home/about/quick-facts-sdo-eve/ EVE] observation of the | ||
| Line 93: | Line 91: | ||
We can conclude that yes, this was a remarkably slow-rising event, but no, it probably did not break the | We can conclude that yes, this was a remarkably slow-rising event, but no, it probably did not break the | ||
flare paradigm particularly. | flare paradigm [ref. 1] particularly. | ||
The AIA images show that the | The AIA images show that the western ribbon probably was obscured by the limb, and the initial excitation | ||
in the | in the eastern ribbon by RHESSI and the He II line was as expected; the later emission from the corona (in both bands) | ||
shows the development of the standard loop prominence system usually associated with a CME. | shows the development of the standard loop prominence system usually associated with a CME. | ||
This was an active-region event, which makes its slow rise still more unusual. | This was an active-region event, which makes its slow rise still more unusual. | ||
| Line 101: | Line 99: | ||
with filament eruptions outside the active latitudes. | with filament eruptions outside the active latitudes. | ||
In extreme cases such events may become [http://sprg.ssl.berkeley.edu/~tohban/wiki/index.php/STEREO_observed_stealth_CME "stealth CMEs"]. | In extreme cases such events may become [http://sprg.ssl.berkeley.edu/~tohban/wiki/index.php/STEREO_observed_stealth_CME "stealth CMEs"]. | ||
== References == | |||
[1] [http://sprg.ssl.berkeley.edu/~hhudson/presentations/coolstars.061106/hudson-micela.pdf Alternative Solar Paradigms for Stellar Flare Activity] (.pdf file) | |||
Latest revision as of 17:21, 22 August 2018
| Nugget | |
|---|---|
| Number: | 180 |
| 1st Author: | Sam Freeland |
| 2nd Author: | Hugh Hudson |
| Published: | 23 July 2012 |
| Next Nugget: | Dense Loop Flares |
| Previous Nugget: | Dimmings and Sustained Gamma-Ray Events |
Introduction
A remarkable flare, distinguishable by its very slow rise phase, has just occurred (SOL2012-07-17T17:15, M1.7) near the west limb of the Sun. According to the NOAA database for the GOES X-ray photometers, using the standard definitions of start and peak time, it took this flare 5.2 hours to develop fully in the 1-8 Å soft X-ray band. We show an overview from AIA and RHESSI in Figure 1. Please refer to the extensive movies showing many dynamic features of this event.

A skeptic might want to describe this very long-rise GOES event as a coincidental superposition of weaker events, perhaps on different parts of the Sun, but in fact the AIA movies linked above, and the RHESSI imaging, show that the entire flare evolution consisted of a single organic process. A search of the GOES database reveals that in fact this event had the longest start-to-peak time interval of any M or X-class flare in the present Hale cycle, in fact since 1995 (FIgure 2).
What else went with this event?
Because this flare was a major gradual event, we might expect a CME to have occurred. This happens with about half of the M-class flares, and it happened this time as well (see the movies pages). Furthermore, since this flare occurred near the west limb, an associated CME almost always means an SEP - a solar energetic particle event. This too was observed. Finally, even better, another (more powerful and more impulsive) flare occurred about a day and a half later (SOL2012-07-19, M7.7), in the same active region. In such a case we may see "CME cannibalism", a phenomenon that may occur when a later faster ejection overtakes an earlier slow ejection out in the heliosphere, in this case about halfway between the Sun and the orbit of Earth. That prediction, if fulfilled (or not), could lead to a future Nugget!
Energetics
Such an event may appear to have no impulsive phase; that is, no hard X-ray and microwave signatures of powerful energy release into non-thermal particle acceleration. The non-impulsive behavior here may or may not reflect the presence of non-thermal particles, though, simply because the longer time scale of the event may make them less detectable This event, well-observed by both RHESSI and Fermi in hard X-rays, provides an excellent test case for this question: can slow CMEs also be associated with non-thermal energy release? A detailed study of these comprehensive data would be rewarding. In a sense the answer is obvious, because we can see the SEPs. But do we see hard X-rays and/or microwaves from the flare itself, as well? Figure 3 shows time series of GOES, the GOES temperature, and the EVE observation of the He II 304 A line (the line that dominates the AIA image shown in Figure 1). The temperatures show several peaks approaching 10 MK, consistent with this being a normal flare but one with slow modulations of its development; the He II data provide indirect evidence for the existence of non-thermal particles exciting chromospheric emissions.
Conclusion
We can conclude that yes, this was a remarkably slow-rising event, but no, it probably did not break the flare paradigm [ref. 1] particularly. The AIA images show that the western ribbon probably was obscured by the limb, and the initial excitation in the eastern ribbon by RHESSI and the He II line was as expected; the later emission from the corona (in both bands) shows the development of the standard loop prominence system usually associated with a CME. This was an active-region event, which makes its slow rise still more unusual. Often, especially at solar minimum, we see large, slow, and relative cool flare-like events associated with filament eruptions outside the active latitudes. In extreme cases such events may become "stealth CMEs".
References
[1] Alternative Solar Paradigms for Stellar Flare Activity (.pdf file)