Flare Observed by a Dozen Instruments: Difference between revisions
imported>Hhudson (Created page with "{{Infobox Nugget |name = Nugget |title = Flare Observed by a Dozen Instruments |first_author = Lucia Kleint |second_author = Kevin Reardon |publish_date = July 14, 2014 |previo...") |
imported>Hhudson (initial entry for 230) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
We live in a golden age for research on solar flares, observationally speaking. | We live in a golden age for research on solar flares, observationally speaking. | ||
This statement reflects not only the existence of powerful satellite observatories | This statement reflects not only the existence of powerful satellite observatories | ||
([http://hesperia.gsfc.nasa.gov/rhessi2/ RHESSI, | ([http://hesperia.gsfc.nasa.gov/rhessi2/ RHESSI], | ||
[http://hinode.msfc.nasa.gov/ Hinode], | [http://hinode.msfc.nasa.gov/ Hinode], | ||
[http://science.nasa.gov/missions/sdo/ SDO], | [http://science.nasa.gov/missions/sdo/ SDO], | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[http://iris.lmsal.com/ IRIS], | [http://iris.lmsal.com/ IRIS], | ||
as well as basic standbys such as | as well as basic standbys such as | ||
[http://www.swpc.noaa.gov/today.html GOES], | [http://www.swpc.noaa.gov/today.html GOES]), | ||
but also advanced ground-based instrumentation at observatories such as | but also advanced ground-based instrumentation at observatories such as the powerful | ||
[http://www.nso.edu/ NSO] | [http://www.arcetri.astro.it/ Arcetri]/[http://www.nso.edu/ NSO] | ||
[http://www.arcetri.astro.it/science/solare/IBIS/ IBIS] instrument. | |||
limited of course by observatory longitudes and the resulting day/night problem. | limited of course by observatory longitudes and the resulting day/night problem. | ||
In addition many spacecraft also observe the interplanetary consequences of a solar eruption. | In addition many spacecraft also observe the interplanetary consequences of a solar eruption. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 40: | ||
All of the observatories listed above got some data, mostly with good coverage and with correct pointing. | All of the observatories listed above got some data, mostly with good coverage and with correct pointing. | ||
A high-resolution observatory can often miss a big flare simply by staring at the wrong spot. | A high-resolution observatory can often miss a big flare simply by staring at the wrong spot. | ||
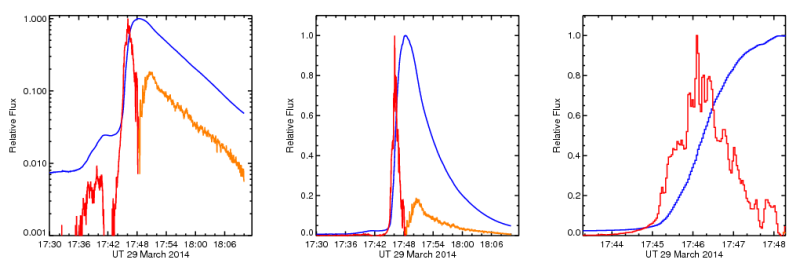
For general reference we offer Figure 1, showing the basic | |||
[http://www.swpc.noaa.gov/today.html GOES] time history. | |||
[[Image:230f1.png|800px|thumb|center|'''Figure 1''': Three different views of the basic time-series soft X-ray data for the flare, from | |||
[http://www.noaa.gov/ NOAA's] | |||
[http://www.swpc.noaa.gov/today.html GOES]. | |||
The plots show the flux (blue), its time derivative (red and gold), and a blow-up of four minutes in the impulsive phase. | |||
The left panel is a standard log-scaled plot, and the right two are more direct linear scalings. | |||
The sign of the time derivative is reversed (the gold) where it turns negative. | |||
Note the presence of impulsive-phase pulsations and likely oscillatory variations in the gradual phase. | |||
]] | |||
== What's really new == | == What's really new == | ||
| Line 50: | Line 62: | ||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corona corona]. | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corona corona]. | ||
== Conclusions == | == Conclusions == | ||
Revision as of 16:25, 7 July 2014
| Nugget | |
|---|---|
| Number: | 230 |
| 1st Author: | Lucia Kleint |
| 2nd Author: | Kevin Reardon |
| Published: | July 14, 2014 |
| Next Nugget: | TBD |
| Previous Nugget: | RHESSI is Annealing Now |
Introduction
We live in a golden age for research on solar flares, observationally speaking. This statement reflects not only the existence of powerful satellite observatories (RHESSI, Hinode, SDO, Fermi, STEREO, and now IRIS, as well as basic standbys such as GOES), but also advanced ground-based instrumentation at observatories such as the powerful Arcetri/NSO IBIS instrument. limited of course by observatory longitudes and the resulting day/night problem. In addition many spacecraft also observe the interplanetary consequences of a solar eruption. Count the instruments up and one quickly exceeds a dozen; these instruments individually mostly have unique capabilities and people cheerfully write papers about their particular individual discoveries. Put them all together and one has a wonderful opportunity to gain a broad insight into flare development, if fortune smiles and many actually have suitable coverage.
Just about that situation happened on March 29, 2014, when SOL2014-03-29 (X1.0) occurred; see the SDO movies.
All of the observatories listed above got some data, mostly with good coverage and with correct pointing. A high-resolution observatory can often miss a big flare simply by staring at the wrong spot. For general reference we offer Figure 1, showing the basic GOES time history.
What's really new
The newest participant is the IRIS spacecraft, the first really to target the "interface region" bridging the gap between the hot surface of the Sun (the photosphere) and the very hot corona.
Conclusions
It often happens that a major flare happens and everybody in the community scrambles to write a "gee whiz" paper about the particularly noteworthy thing their instrument has seen. Often, of course, they include as much data from other sources as possible, and of course they work hard at drawing physically meaningful conclusions. Nevertheless they tend to work simultaneously and not necessarily in a coordinated way, and what appears in the literature may be disorganized as a result. Only seldom does the community do a retrospective look at a given well-observed event, but we recommend that here because of the excellent coverage.
References
[1] [ ""]